Zirconia Blocks: A Practical Guide for Dental Labs and Distributors
2025-09-22
Zirconia blocks have become a cornerstone material in modern dentistry, offering labs and distributors a unique combination of strength, aesthetics, workflow efficiency, and market demand. This guide provides a structured overview to help labs optimize production and distributors enhance product offerings.
Module 1: Understanding Zirconia Blocks
Definition:
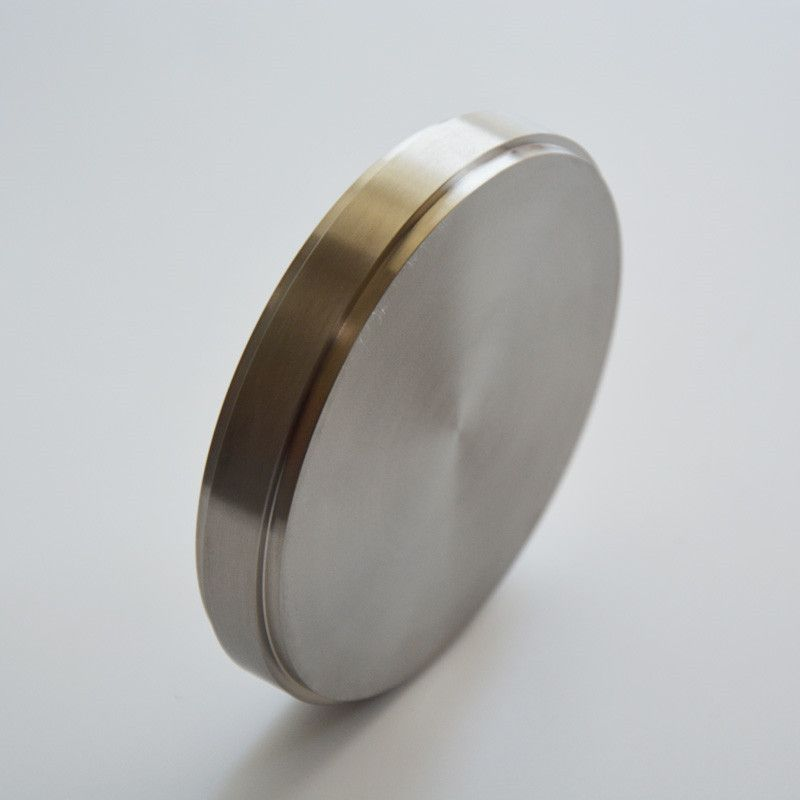
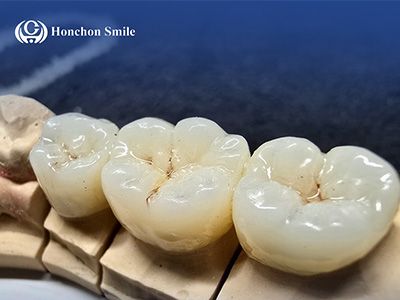
Zirconia blocks are high-strength, biocompatible dental ceramics, primarily used for crowns, bridges, veneers, and implant-supported restorations.
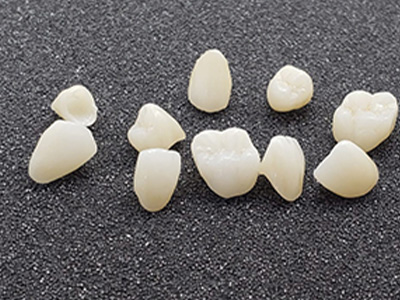
Available as white blocks, pre-shaded blocks, or multilayer/colored blocks.
Key Advantages for Labs & Distributors:
High fracture resistance → fewer remakes.
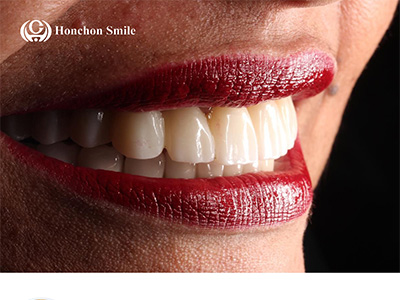
Tooth-like aesthetics → high patient satisfaction.
CAD/CAM compatibility → precision milling and efficient workflow.
Versatile product line → meets a wide range of restorative indications.
Module 2: Types of Zirconia Blocks
| Type | Typical Use | Strength | Aesthetic | Workflow Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
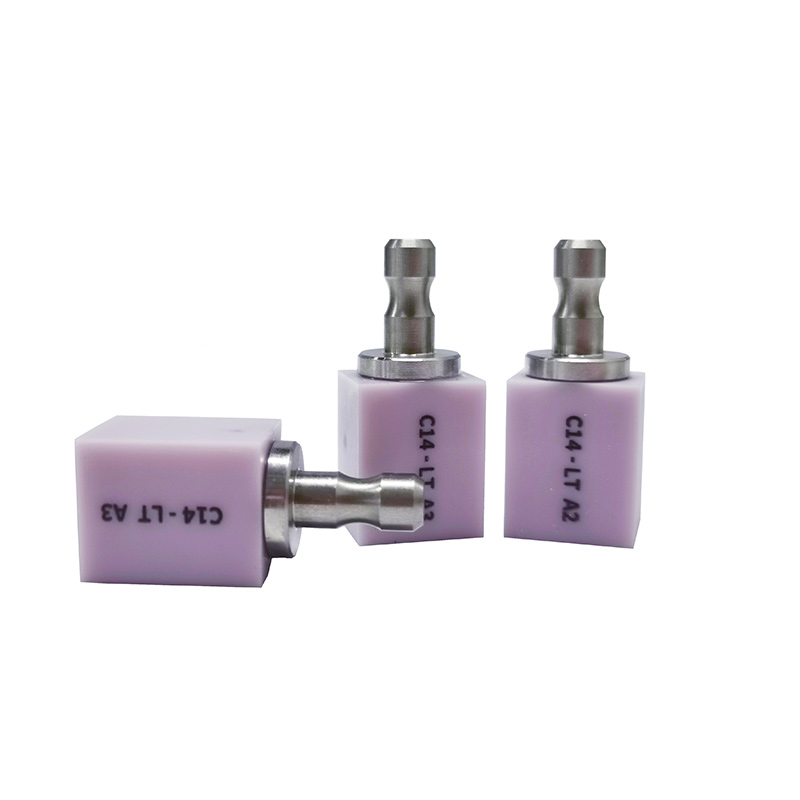
| White Zirconia | Posterior crowns, bridges | High | Moderate | Affordable, easy to customize |
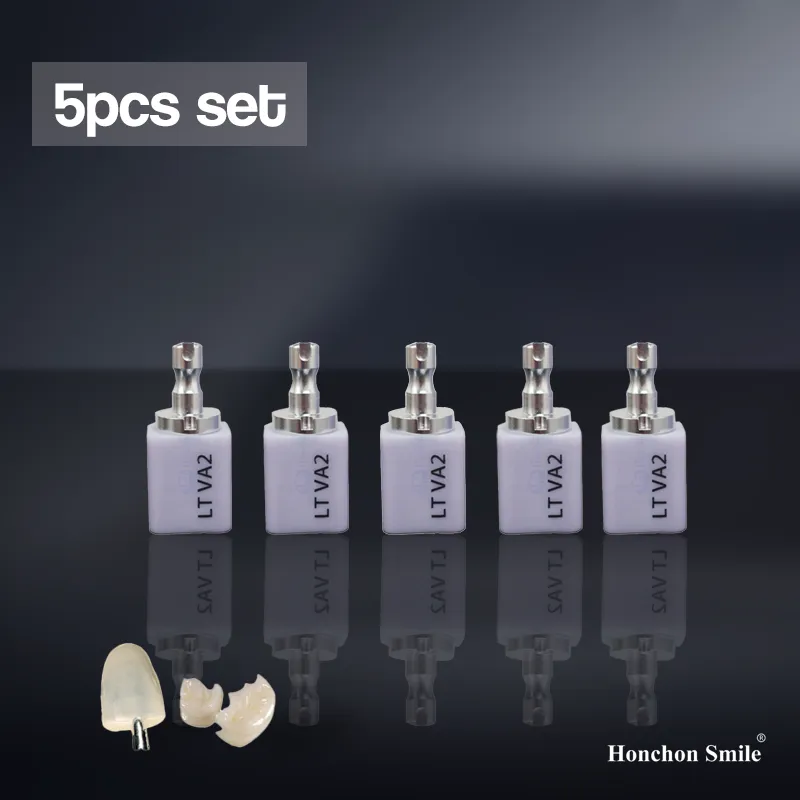
| Pre-Shaded Zirconia | Anterior and posterior restorations | High | High | Saves staining step, consistent shade |
| Multilayer Zirconia | Full-contour, single-visit restorations | Moderate to High | Very High | Natural gradient, minimal adjustments |
Tip for Labs: Maintain a balanced inventory covering all three types to handle diverse restoration cases efficiently.
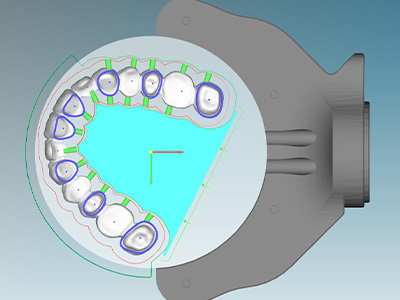
Module 3: Integration with CAD/CAM Workflows
Precision Milling: Compatible with most open or closed CAD/CAM systems.
Digital Design: Pre-shaded and multilayer blocks reduce chairside adjustments.
High-Throughput Production: Monolithic zirconia enables fast milling for high-volume labs.
Tip for Distributors: Emphasize compatibility with popular CAD/CAM systems when selling to labs; provide technical guidance for integration.
Module 4: Future Trends Labs and Distributors Should Watch
Ultra-Translucent Zirconia: Closer to natural enamel, premium product for anterior restorations.
Variable-Strength Blocks: Allows labs to select strength based on restoration location.
Bioactive & Antibacterial Zirconia: Potential to improve osseointegration and reduce peri-implantitis risk.
Sustainability: Energy-efficient production and recycling of zirconia dust can reduce costs and appeal to eco-conscious clients.
Module 5: Practical Recommendations for Labs
Use pre-shaded or multilayer blocks for efficiency and consistent aesthetics.
Keep high-strength zirconia for posterior restorations; ultra-translucent for anterior cases.
Maintain CAD/CAM compatibility for faster workflow and fewer adjustments.
Stock a variety of sizes, shades, and translucency levels to minimize production delays.
Module 6: Recommendations for Distributors
Highlight strength, aesthetics, and workflow efficiency to clinics and labs.
Promote CAD/CAM compatibility as a key selling point.
Offer technical support and training for labs to increase customer loyalty.
Introduce premium zirconia products to differentiate from competitors.
Module 7: Conclusion
Zirconia blocks are more than a dental material—they are a strategic asset for labs and distributors. By understanding the different types, integrating with CAD/CAM workflows, and keeping an eye on future developments, labs can enhance productivity, and distributors can maximize sales and client satisfaction.
Tags: zirconia blocks, dental labs, dental distributors, CAD/CAM dentistry, high-translucent zirconia, monolithic zirconia, pre-shaded zirconia