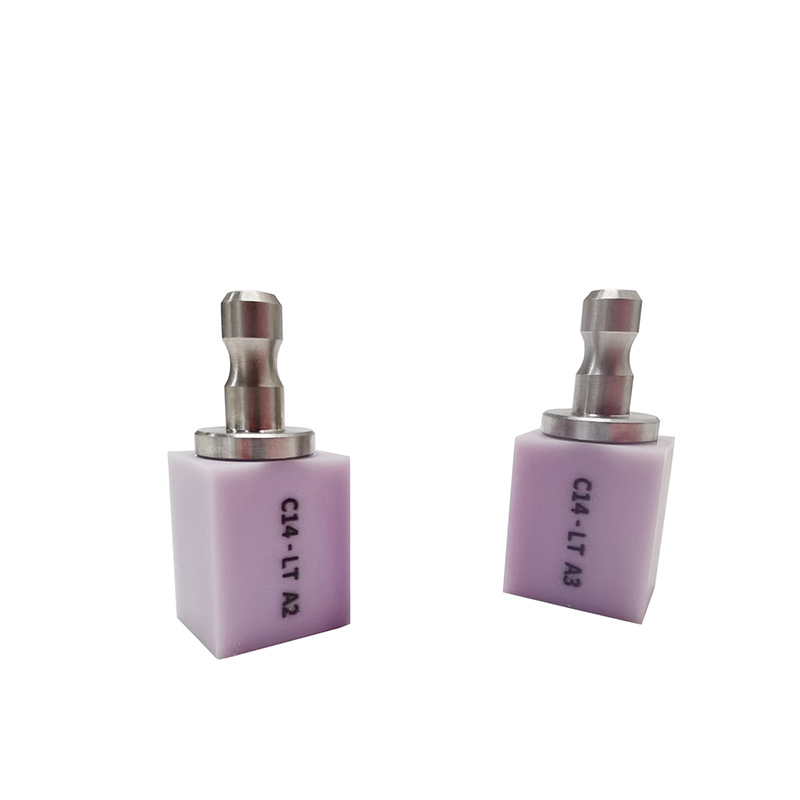
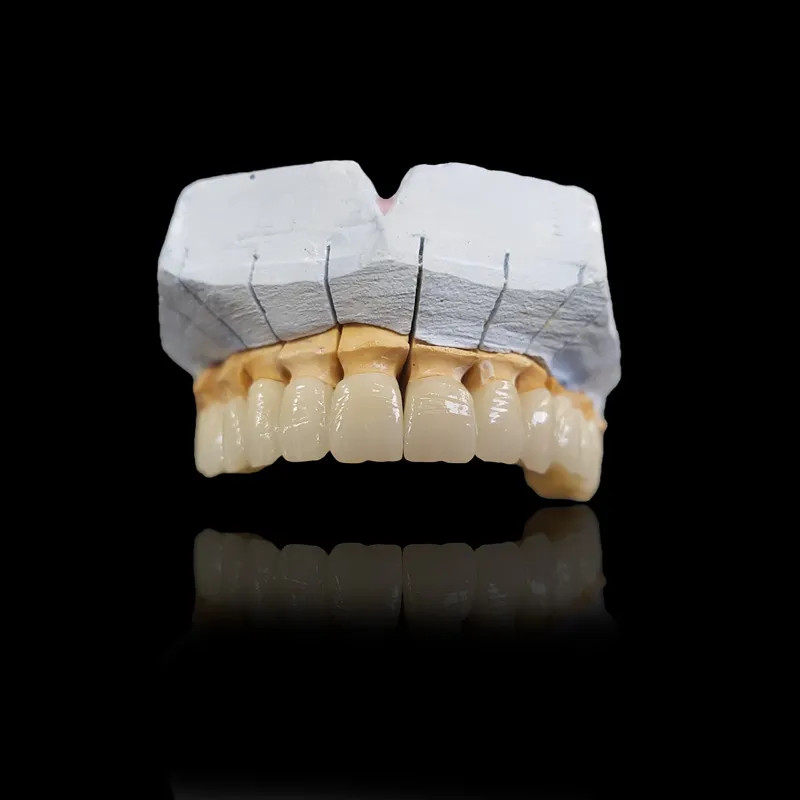
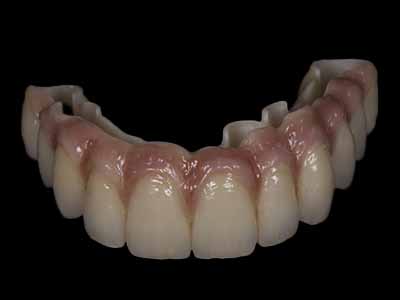
The Role of Lithium Disilicate in Modern Restorative Dentistry
2025-07-07
Introduction
In the ever-evolving field of restorative dentistry, material innovation plays a crucial role in improving clinical outcomes and patient satisfaction. Among the many options available, lithium disilicate has stood out as a high-performance glass-ceramic material that blends strength, aesthetics, and versatility. Widely used for crowns, veneers, inlays, and onlays, lithium disilicate supports both traditional and digital workflows, making it a favorite among dental professionals worldwide. This article explores the advantages, clinical applications, and future potential of lithium disilicate in modern dentistry.

What is Lithium Disilicate?
Lithium disilicate (Li₂Si₂O₅) is a type of glass-ceramic material composed primarily of lithium, silica, and other mineral additives. Known for its unique microstructure featuring densely packed needle-like crystals, lithium disilicate combines high flexural strength (360–500 MPa) with excellent translucency, allowing it to mimic the natural aesthetics of enamel and dentin.
Originally introduced for heat-pressed ceramics, lithium disilicate is now also available in CAD/CAM blocks, making it compatible with modern digital workflows such as chairside milling and same-day restorations.
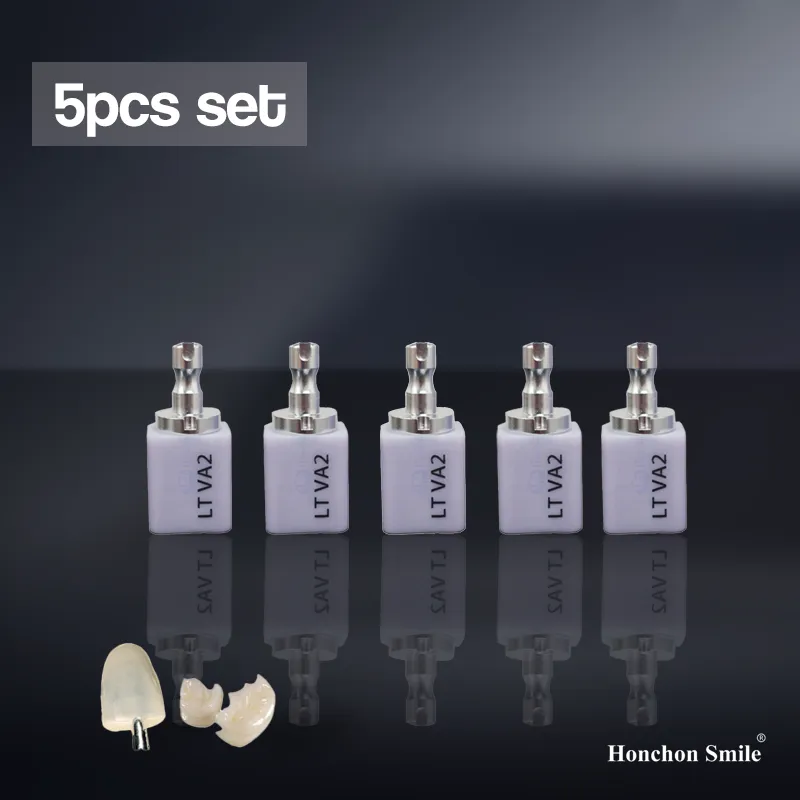

Key Advantages of Lithium Disilicate
1. Superior Aesthetics
Lithium disilicate offers a high level of translucency, allowing restorations to closely resemble natural teeth. Its ability to reflect and refract light makes it ideal for restorations in the aesthetic zone, such as anterior crowns and veneers.
2. High Strength and Durability
With flexural strength reaching up to 500 MPa after crystallization, lithium disilicate is strong enough to be used in single-unit crowns, inlays, and even three-unit bridges in the anterior region. This durability ensures long-lasting results.
3. Versatile Indications
The material is suitable for a wide range of clinical uses, including:
Veneers
Full-contour crowns
Partial crowns (inlays/onlays)
Three-unit bridges (up to premolar)
Implant-supported crowns
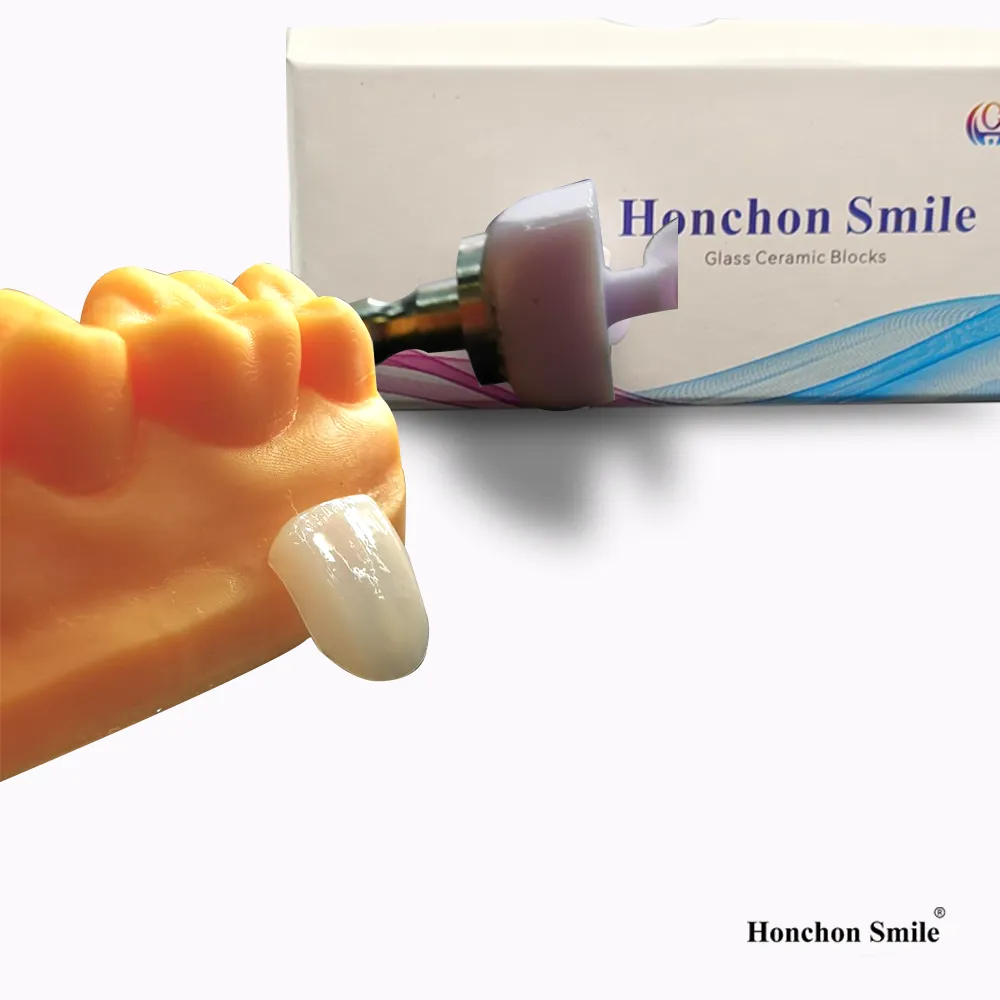
4. Minimally Invasive Preparation
Thanks to its high strength and bonding capacity, lithium disilicate restorations can be made thinner, allowing for conservative tooth preparation. This preserves more natural tooth structure and reduces trauma.
5. Excellent Bonding Ability
Lithium disilicate can be etched and bonded using resin cements, providing a strong chemical bond to the tooth surface. This improves marginal integrity and retention, reducing the risk of debonding or microleakage.
6. CAD/CAM Compatibility
Modern lithium disilicate blocks are optimized for digital dentistry. They can be milled chairside using in-office systems or processed in dental labs using CAM equipment. After milling, a crystallization firing is performed to achieve final strength and aesthetics.
7. Color Variety and Shade Matching
Available in multiple translucency levels (HT, MT, LT) and VITA classic shades, lithium disilicate allows precise color matching for customized restorations without staining or layering.
Common Applications of Lithium Disilicate in Dentistry
1. Anterior and Posterior Crowns
Due to its natural appearance and strength, lithium disilicate is widely used for full-contour crowns in both anterior and posterior regions.
2. Veneers
Its excellent translucency makes lithium disilicate perfect for minimally invasive veneers, improving aesthetics while preserving enamel.
3. Inlays and Onlays
Lithium disilicate can be used for partial restorations that restore form and function without requiring full crown coverage.
4. Implant-Supported Restorations
For aesthetic areas, lithium disilicate provides a reliable option for implant crowns, especially where soft tissue esthetics are a priority.
5. Three-Unit Bridges (Anterior)
When properly designed, lithium disilicate can be used for short-span anterior bridges, offering both strength and beauty.
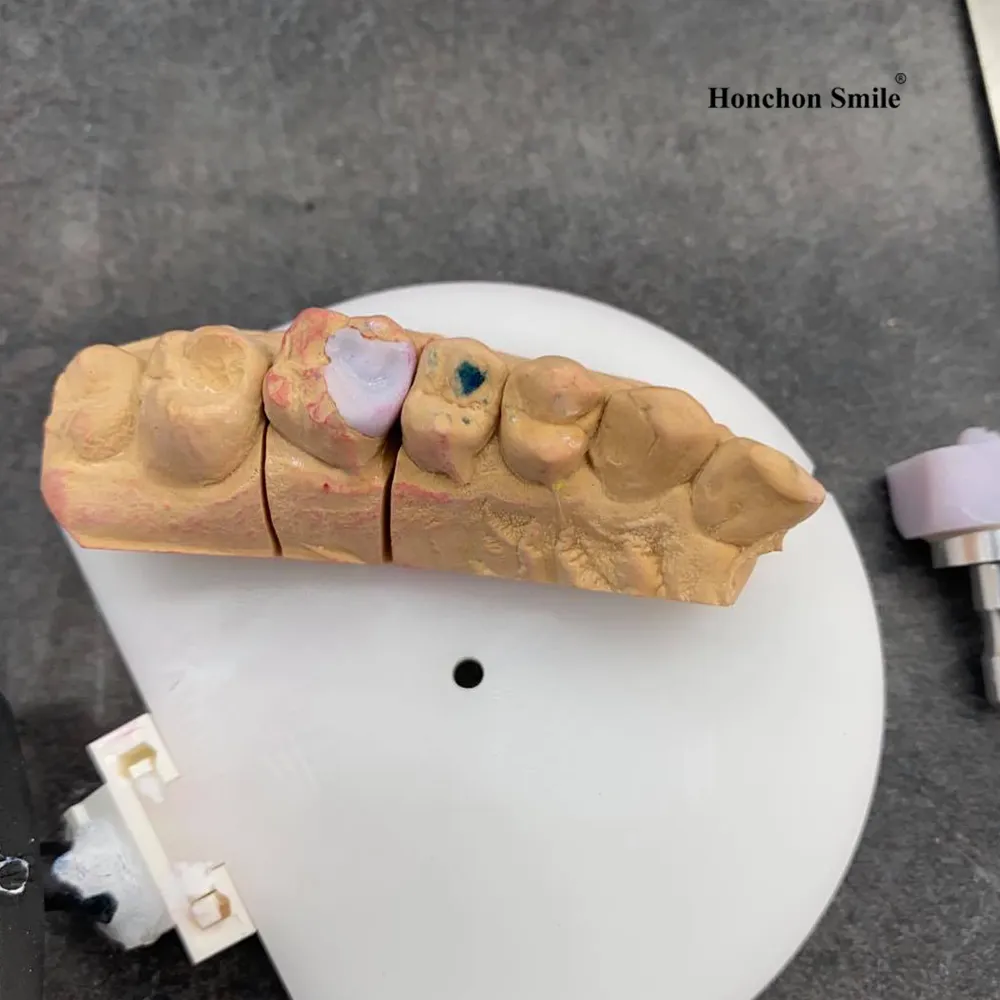

The Future of Lithium Disilicate
Ongoing advancements in digital workflows and material science continue to expand the use of lithium disilicate. Research is focused on:
Enhancing translucency without compromising strength
Improving wear resistance and fracture toughness
Developing faster crystallization cycles
Expanding shade options for better customization
In addition, AI-driven design software, 3D printing integration, and improved bonding protocols are helping clinicians achieve even more efficient and predictable results with lithium disilicate.
Conclusion
Lithium disilicate has earned its place as a gold standard in modern restorative dentistry. Its ideal balance of aesthetics, strength, and versatility allows it to meet the demands of both clinicians and patients. As dentistry becomes increasingly digitized, lithium disilicate’s compatibility with CAD/CAM systems ensures it remains a reliable and efficient material choice for a wide range of restorative applications.
By understanding its properties and possibilities, dental professionals can leverage lithium disilicate to deliver natural-looking, long-lasting restorations that enhance both smiles and clinical success.