Zirconia block manufacturing process in-depth analysis
2025-05-27
I. Core manufacturing process
Raw material preparation
Stabilizer doping: Add 3 mol% Y₂O₃ (yttrium oxide) as tetragonal phase stabilizer to inhibit the volume expansion caused by monoclinic phase transition.
Nanopowder synthesis: Synthesize ZrO₂ powder with particle size ≤50nm by co-precipitation method or hydrothermal method to ensure grain uniformity.
Powder treatment and molding
Spray granulation: Add PVA (polyvinyl alcohol) binder and form microspheres with excellent fluidity (particle size 80-150μm) by centrifugal atomization.
Dry compression molding: press the blanks under pressure ≥200MPa, and control the density deviation within ±0.1g/cm³.
Cold Isostatic Pressing Strengthening: Eliminate interlayer density difference by uniform pressure application at 200-300MPa (key process).
Pre-sintering and precision processing
Pre-sintering parameters: 900-1100°C low temperature pre-sintering to form a porous structure (density of about 50%), which is easy to cut and mold.
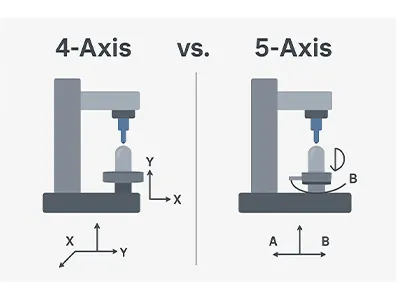
CAD/CAM machining:
Cutting accuracy ≤25μm (5-axis machine)
Compensation of sintering shrinkage 20-25% after cutting (patented algorithm by Wieland)
High temperature sintering and strengthening
Peak sintering temperature: 1350-1550°C (adjusted according to brand process differences), holding time 2-4 hours to achieve densification.
HIP post-treatment:
Hot Isostatic Pressure (HIP) at 1300°C/100MPa under argon environment, porosity reduced to <0.02%
Surface treatment and aesthetic optimization
Nanoscale polishing: use diamond grinding paste (particle size 0.1-0.5μm) to polish to Ra ≤ 0.05μm.
Gradient Dyeing Technology: Penetrating dyeing solution to achieve A1-A3 transparency gradient (Eltron Multi-layer Stacking Technology).
Comparison of key process parameters
Process link Imported brand parameters (Weiland) Domestic brand parameters (Aerotron)
Powder particle size ≤30nm (SEM detection) ≤50nm (laser particle size meter detection)
Sintering temperature 1450℃±10℃ (gradient sintering) 1380℃±20℃ (conventional sintering)
Flexural strength Flexural strength ≥1400MPa (ISO 6872 certification) ≥1200MPa (national standard YY0716 requirements)
Third, the process difficulties and solutions
Crack control:
pre-sintering stage using stepped temperature (100 ℃ / h → 50 ℃ / h) to reduce the thermal stress
Cutting path optimization to avoid stress concentration (Zekang five-axis path compensation algorithm) (Zeccon 5-axis path compensation algorithm)
Color stability:
Sintering atmosphere control (oxygen partial pressure ≤10-⁶Pa) to prevent Y₂O³ decomposition and discoloration
Precise control of dye penetration depth (error ±0.1mm)
Emerging process breakthroughs
Microwave sintering:
Sintering time reduced by 50% (Wieland lab data)
Grain size uniformity increased by 30% (SEM observation)
Additive Manufacturing:
Light-curing 3D printing of zirconia paste, layer thickness accuracy of 20μm (Densburg Sirona pilot phase)
Note: Differences in process parameters directly affect the transmittance (A1-A3 grading) and mechanical properties of zirconia blocks, clinical selection should be combined with branded real-world data (e.g., VITA Easyshade testing).