Zirconia Blocks for Dental Restorations: 10 Expert Facts You Won’t Find on Most Manufacturer Sites
2025-11-19
Introduction
Zirconia blocks have revolutionized the world of dental restorations with their unmatched strength, biocompatibility, and esthetic potential. Yet, most information available online focuses on basic features — leaving dental professionals with unanswered questions when choosing the right block.
This guide cuts through the noise and delivers 10 must-know expert-level facts about dental zirconia, including materials science, clinical performance, sintering behavior, and what manufacturers don’t usually tell you.
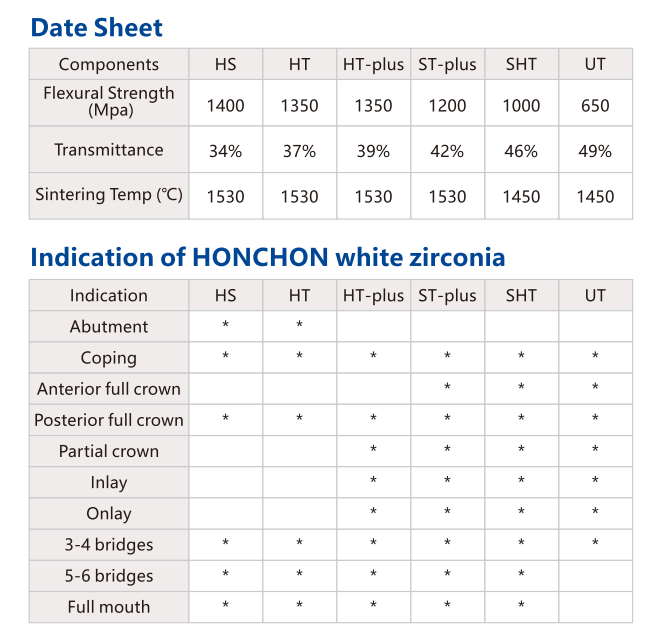
1. Not All Zirconia is Created Equal: Generations Matter
There are at least three generations of dental zirconia — and knowing which one you’re using directly impacts performance.
| Generation | Yttria Content | Flexural Strength | Translucency | Main Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Gen | 3Y-TZP | ~1200--1400 MPa | ~40% | Posterior bridges |
| 2nd Gen | 4Y-PSZ | ~1000 MPa | ~43% | Universal use |
| 3rd Gen | 5Y-PSZ | ~700 MPa | ~49% | Anterior crowns, veneers |
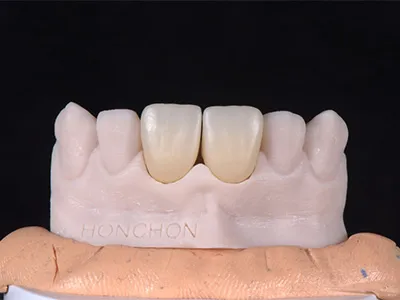
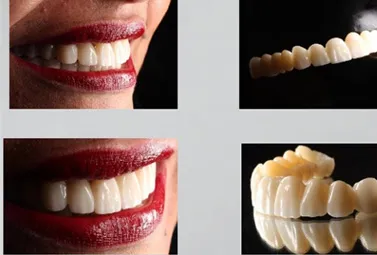
The case in the picture is a 4Y-5Y zirconia block restoration
As shown in the pictures, 4Y and 5Y zirconia blocks perform better in aesthetic performance.
Tip: If a supplier doesn’t clearly state the yttria level, ask them — or they may be mixing layers without consistency.
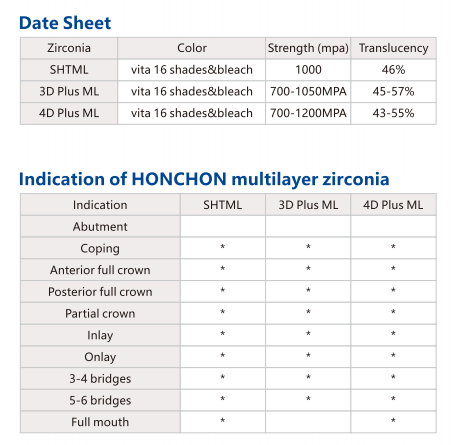
2. Multilayer Zirconia: The Truth About Gradient Technology
Most suppliers now offer multilayer zirconia, but not all multilayers perform the same.
Some blocks only vary in color gradient (aesthetic-only).
High-end multilayers, like Honchon ML-P, vary in mechanical properties (strength gradient via Yttria distribution).
Look for multilayers with layer-by-layer strength mapping if you need both esthetics and durability — especially for long-span bridges.

HONCHON 3D plus permeability and strength diagram of each layer
3. Sintering Parameters Are Not Universal — and Can Cost You
Many labs sinter all zirconia on the same curve — and that’s a mistake.
Different zirconias require different sintering temperatures and holding times.
Fast sintering may work for 3Y zirconia but ruin the translucency of 5Y materials.
Always refer to manufacturer-specific sintering profiles.
Lab Tip: Save your curves in your furnace software and label by block code. It prevents surface roughness, deformation, or cracking.
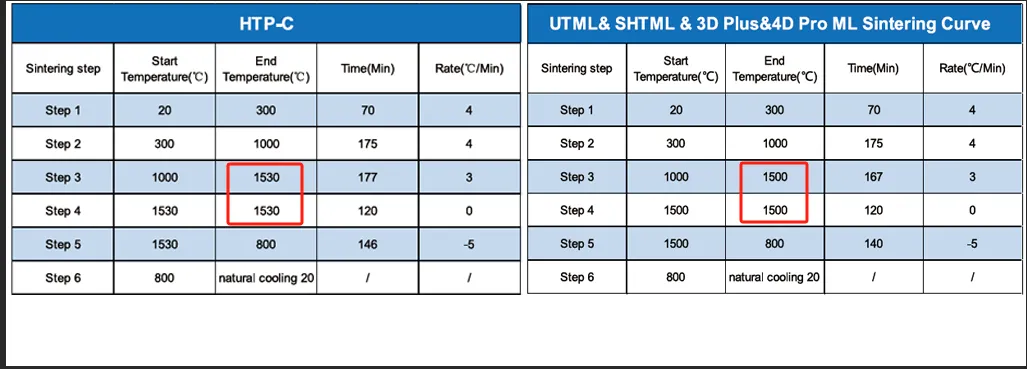
Sintering curves of different types of zirconia blocks
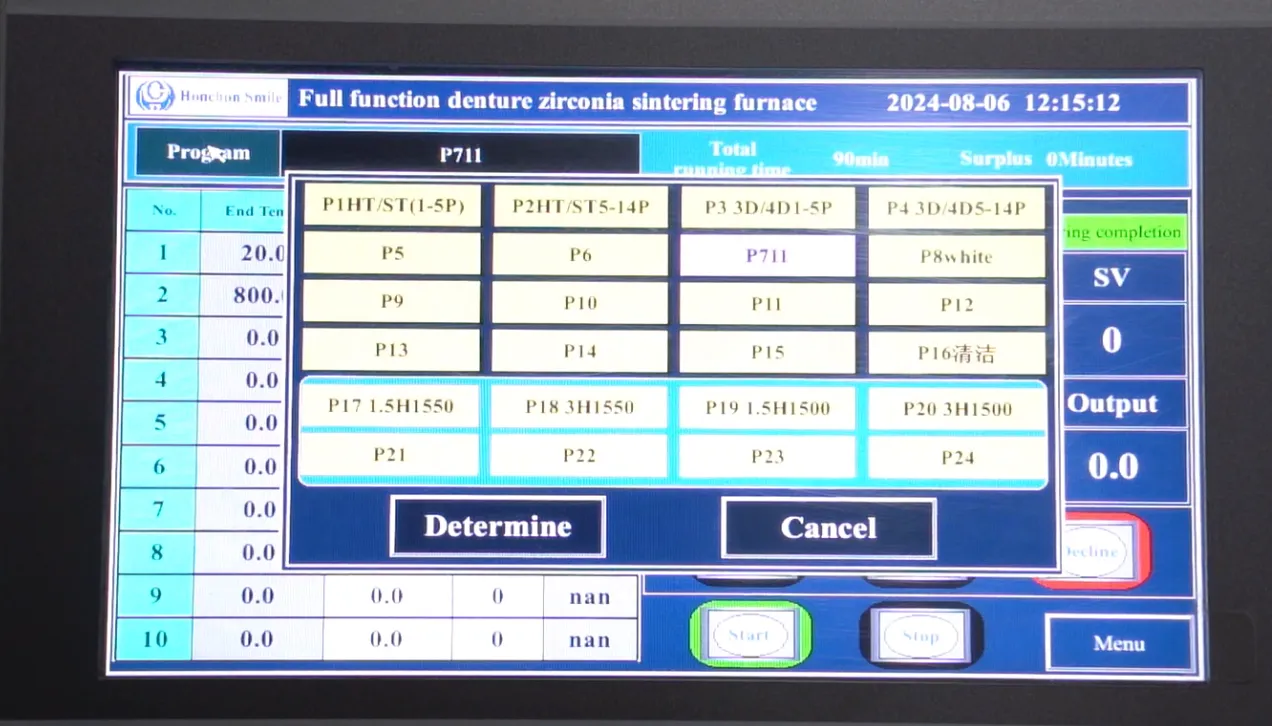
4. Sintering Profiles Matter — But So Does Sintering Equipment
Sintering is not as simple as setting a furnace temperature and walking away.
Different zirconia blocks require specific temperature curves for optimal results. Sintering too quickly can cause cracking, while too slow can lead to surface roughness.
Temperature ramp rates (how quickly the furnace heats up) and holding times are critical — a parameter many dental technicians overlook.
Pro Tip: Invest in a calibrated sintering oven and ensure it’s compatible with the manufacturer's recommended temperature curve. Fine-tuning this ensures the best surface finish and dimensional accuracy.

5. Cutting Performance: Not All Zirconia Is Easy to Mill
Zirconia blocks may feel the same in your hand, but they can behave differently when milled.
High-density zirconia is tougher to mill, requiring specialized diamond-coated burs and high-speed spindles.
Lower-density blocks (like some 3Y and 4Y types) are easier to mill, but they may have issues with edge chipping during the cutting process, especially for fine detail work.
CAD/CAM Tip: Always match the milling strategy to the specific block’s characteristics. Use wet milling when possible for better surface finish.
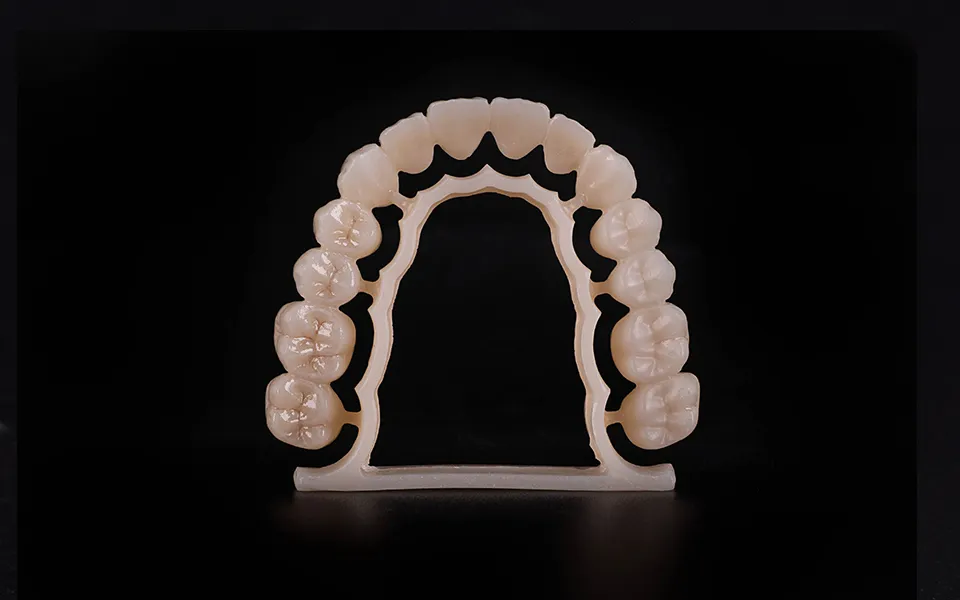
6. Zirconia Is Not Just for Crowns — It's Also for Full-Arch and Implant Restorations
While zirconia blocks are most commonly used for crowns and bridges, their potential goes far beyond that.
Full-arch restorations made with high-strength zirconia (like 3Y or 5Y) are becoming increasingly popular due to their excellent fracture resistance and biocompatibility.
Zirconia also shines in implant abutments thanks to its ability to withstand high occlusal forces without compromising esthetics.
Innovation: Hybrid zirconia blocks (with inner titanium cores) are now available, offering the best of both worlds: strength and flexibility for implants.
7. Biocompatibility Isn’t Just About Tissue Acceptance — It's About Longevity
While zirconia is widely praised for its biocompatibility, there are several factors that determine long-term tissue health.
High-quality zirconia blocks have a very smooth surface after milling and sintering, reducing the risk of tissue irritation or inflammation.
Porosity in low-quality zirconia, however, can trap bacteria, leading to biofilm formation and potential infection.
Laboratory Tip: Always ensure that milling and sintering are done precisely to avoid surface imperfections that may affect biocompatibility.
8. The Future of Zirconia: Reinforced & Hybrid Materials
Zirconia is evolving, and its future lies in reinforced composites and hybrid materials.
Zirconia-reinforced lithium silicate (ZLS) and other composite materials are being developed to combine zirconia’s strength with lithium silicate’s esthetics.
These hybrid materials provide more lifelike restorations that are easier to mill and less prone to fracture.
R&D Trend: Manufacturers are working on bioactive zirconia that can promote tissue regeneration and faster healing post-implantation.
9. Thickness & Porosity: Don’t Overlook These Factors
Thicker blocks can hold up better under occlusal stress, but they also tend to be less translucent, reducing esthetic quality.
Porosity in zirconia can result in compromised mechanical properties. The more homogeneous and dense the zirconia, the more it will stand up to mechanical stress.
Pro Tip: Always check for porosity in the block material during procurement. Ask for a density report or undergo a third-party non-destructive testing before use.
10. Testing & Certification Are Your Best Friend
Just because a block claims high strength or translucency doesn’t mean it’s been rigorously tested.
ISO 13356 tests the hydrothermal aging (how zirconia stands up to moisture over time) and provides insight into its long-term durability.
CE and FDA certifications indicate that the material has passed the required biocompatibility and mechanical standards for dental use.
Certification Tip: When purchasing zirconia blocks, ensure that the blocks are tested for relevant international standards (ISO, CE, FDA). If not available, it may be worth considering other manufacturers.
HONCHON FDA certification, screenshot of FDA official website
FAQs: Everything You Need to Know About Zirconia Blocks
Q1: Can zirconia blocks be used for long-span bridges?
A1: Yes, especially high-strength 3Y or 5Y zirconia blocks. These can support full-arch and long-span restorations without compromising stability.
Q2: How do I prevent chipping when milling zirconia?
A2: Use wet milling with diamond-coated burs for better results. Also, always follow the manufacturer's recommended milling strategy.
Q3: Are zirconia blocks suitable for implant restorations?
A3: Absolutely. Zirconia’s biocompatibility and strength make it ideal for implants and implant-supported restorations.
Q4: How does multilayer zirconia affect restorations?
A4: Multilayer zirconia mimics the natural transition from dentin to enamel, giving both aesthetic and strength benefits, especially for anterior restorations.
Download Our Full Zirconia Material Data Sheet
For more in-depth specifications, sintering curves, and product comparisons, download our Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) below.
CTB231225010CSX-dental zirconia block-MSDS-ENpdf
Conclusion
Choosing the right zirconia block isn’t just about strength or translucency — it's about balancing both while considering the unique demands of your dental restorations. Armed with this expert-level knowledge, you’ll make more informed decisions that not only improve the quality of your work but also contribute to long-lasting patient satisfaction.